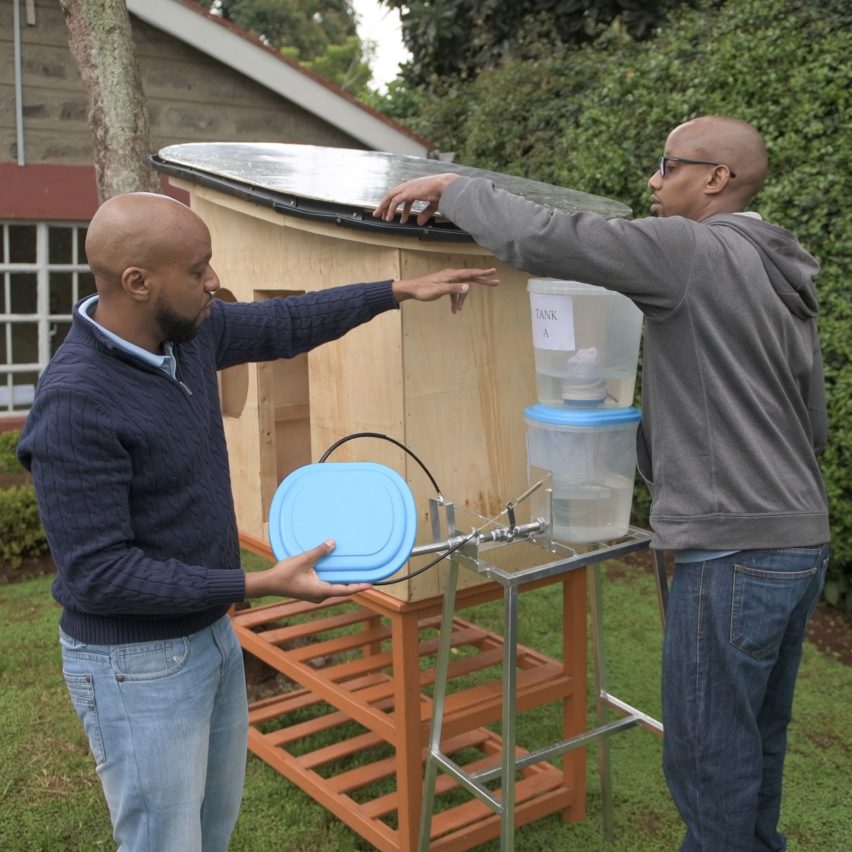
Dezeen promotion: BellTower has been revealed as the winner of the 2020 Lexus Design Award for its design project that could help emerging nations provide their citizens with clean water.
Kenyan studio BellTower's win marks the first time an African designer has ever won the coveted Lexus Design Award in its eight-year history.
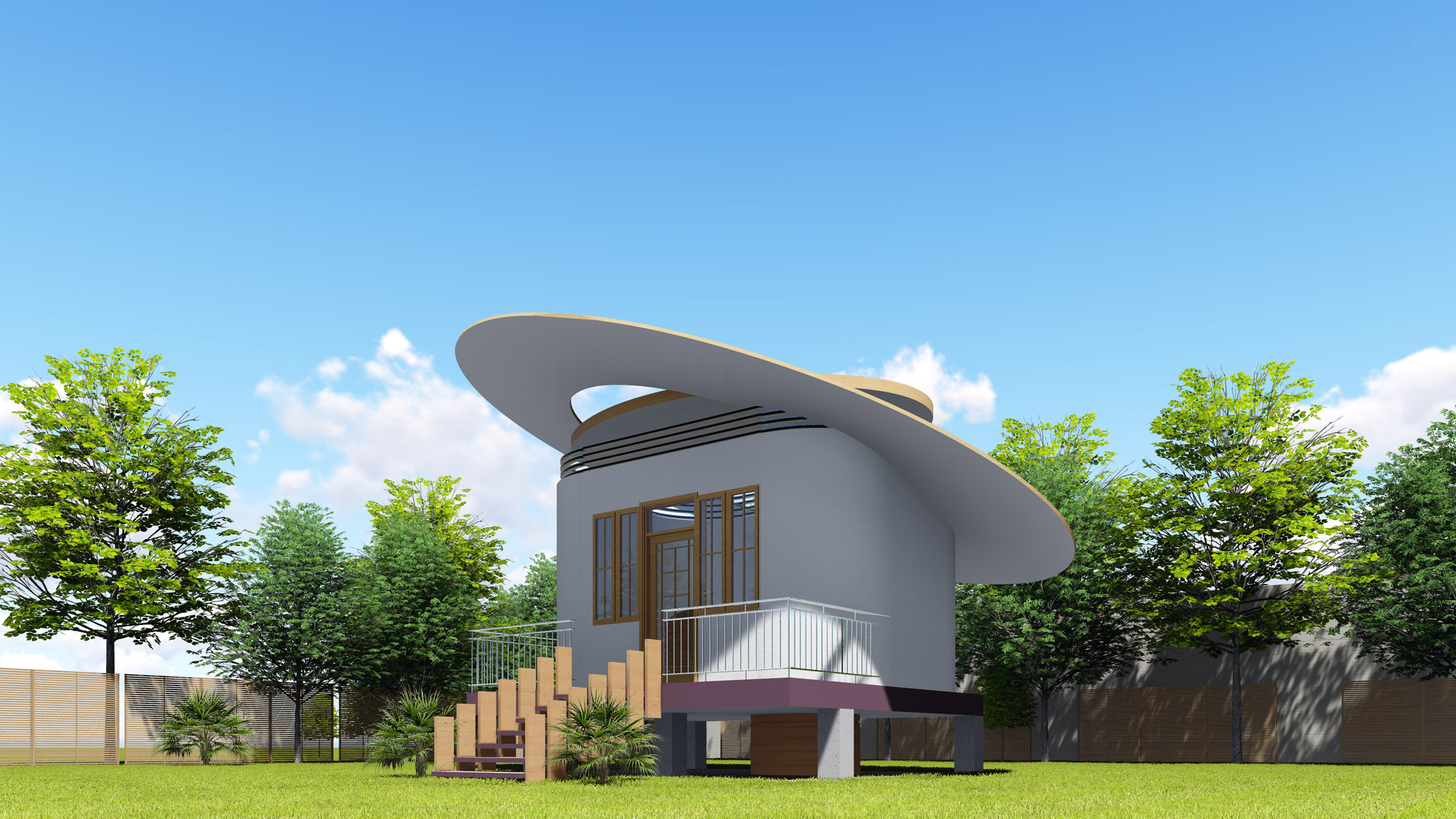
Its winning project, named Open Source Communities, is an affordable structure developed for collecting and storing rainwater for safe drinking. It has been designed specifically for use in developing countries with the aim of helping these nations establish more sustainable communities.
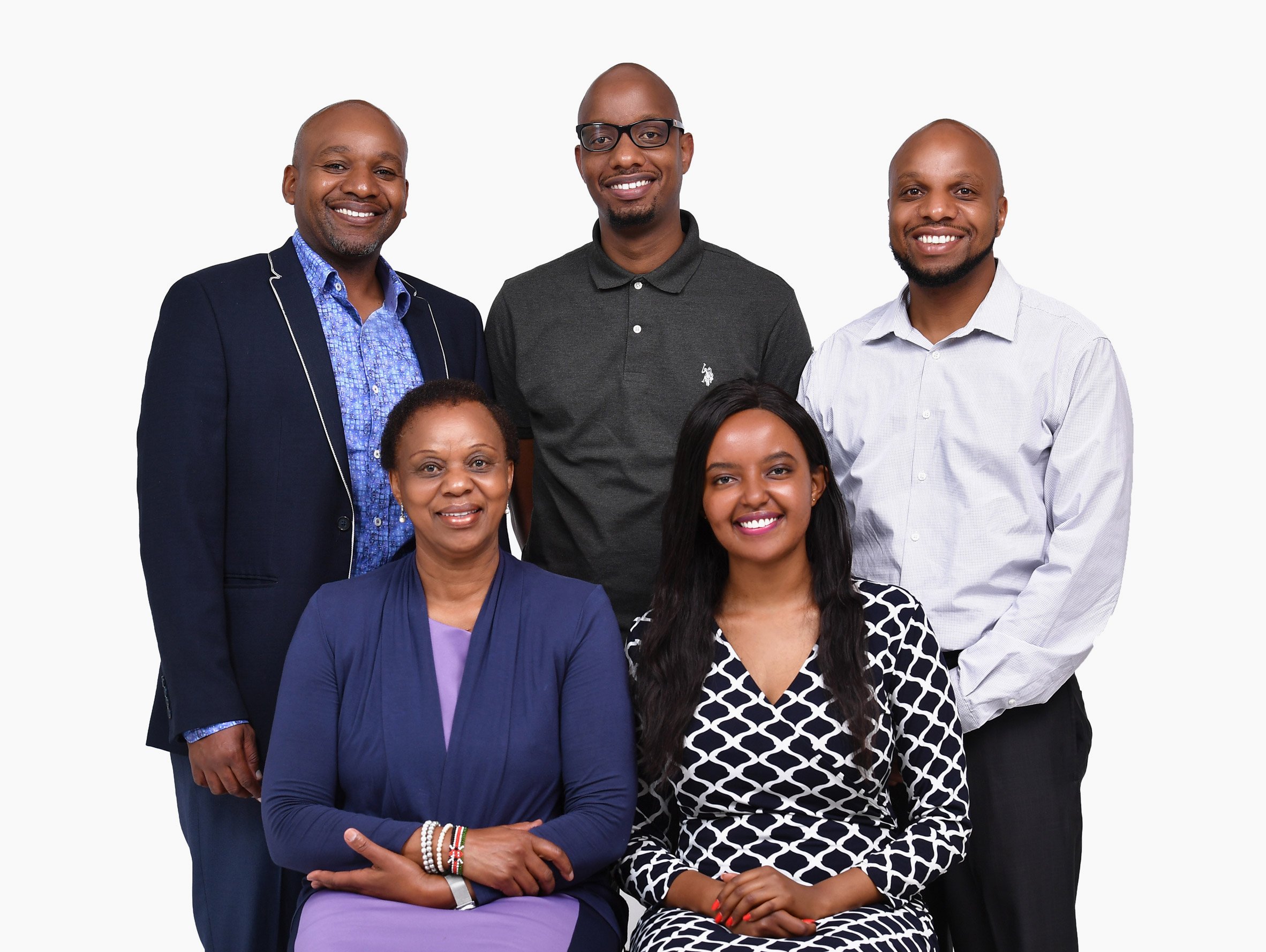

BellTower was founded in Kenya in 2014 by designers John Brian Kamau, Joyce Wairimu Gachiri, Ian Githegi Kamau, Esther Wanjiku Kamau and Arvin Booker Kamau.
The team was selected ahead of five other finalists shortlisted for the prize, including US studio Sutherlin Santo, UK-based duo Théophile Peju and Salvatore Cicero, Chinese designer Yaokun Wu, Russian creative Irina Samoilova and Pakistani industrial designer Aqsa Ajmal.

The decision was made after all six finalists presented their work to this year's panel of judges, which included Paola Antonelli, Jeanne Gang, John Maeda, and Simon Humphries.
This process took place in a virtual venue due to the cancellation of Milan Design Week.
The judging criteria was based on the finalists' efforts to "anticipate, innovate and captivate in the quest for a better tomorrow".
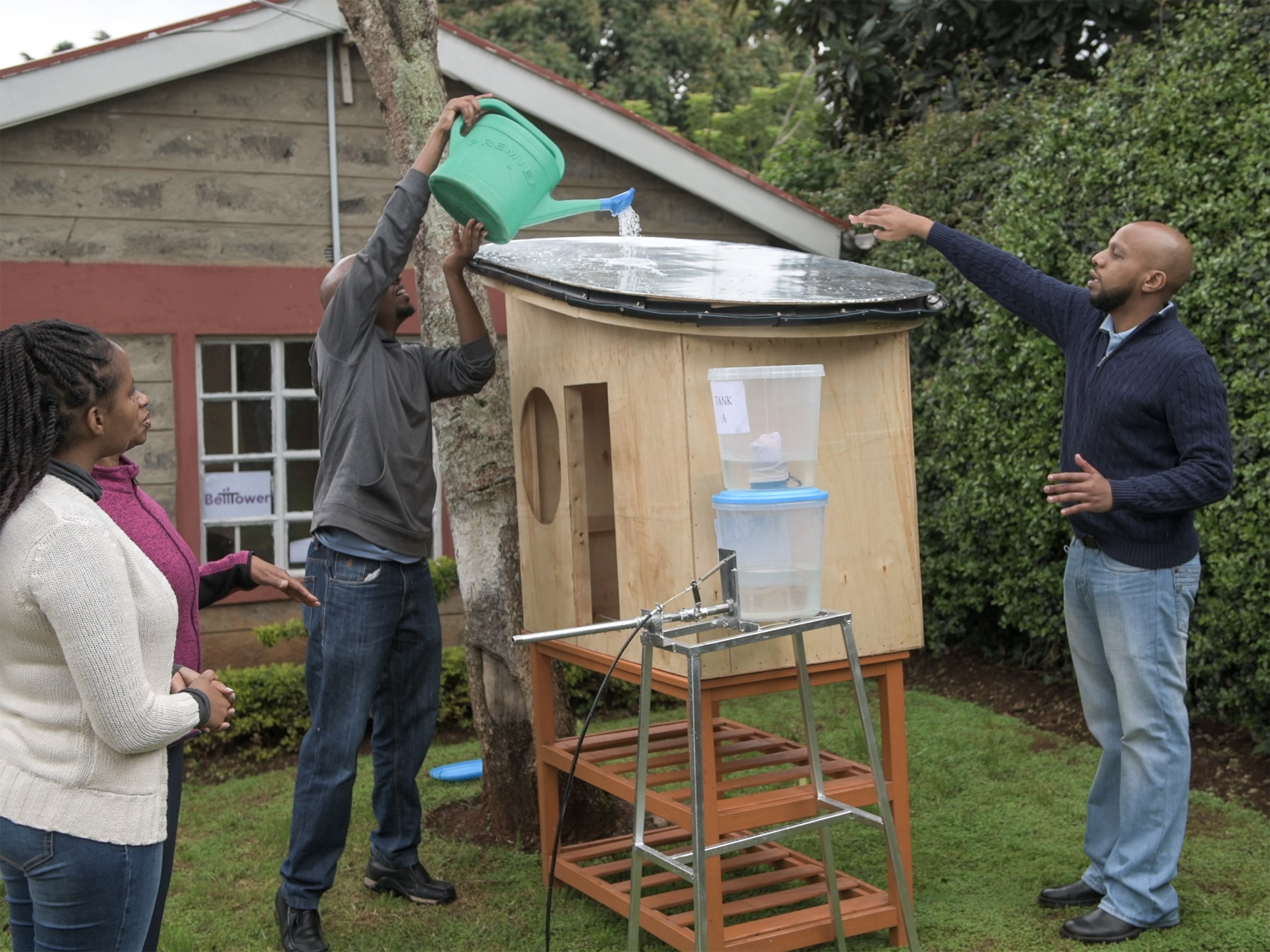

Reflecting on the winning project, Gang said: "The Grand Prix winner expands our definition of design to include systems of finance for community projects and engages the critical role clean drinking water plays in citizens' ability to thrive."
"By addressing the way that the project will come into being and be sustained economically, the designers broaden our thinking about what design is and could be," she added.
"While the project is an apparatus to collect and store rainwater for safe drinking, it is also a financial game plan for empowering a community."

The Lexus Design Award's Grand Prix is a leading international design award that was initiated by luxury vehicles company Lexus in 2013. Its aim is to help nurture the next generation of designers by funding and showcasing their work, and equipping them with the skills to address the challenges of today.
This year the award received over 2000 submissions from 79 different countries. The finalists were announced in January 2020.
Prior to the judging, the six shortlisted designers were flown to New York to participate in a two-day workshop with Lexus at its creative culture space, INTERSECT BY LEXUS - NYC.
Here, they developed their designs through hands-on sessions with well-known designers including Joe Doucet, Bethan Gray, Philippe Malouin, and Shohei Shigematsu, who acted as mentors to help create prototypes of their designs.
After the mentoring session, each finalist received ongoing access to a mentor via one-on-one online sessions as they continued to develop their
prototypes.
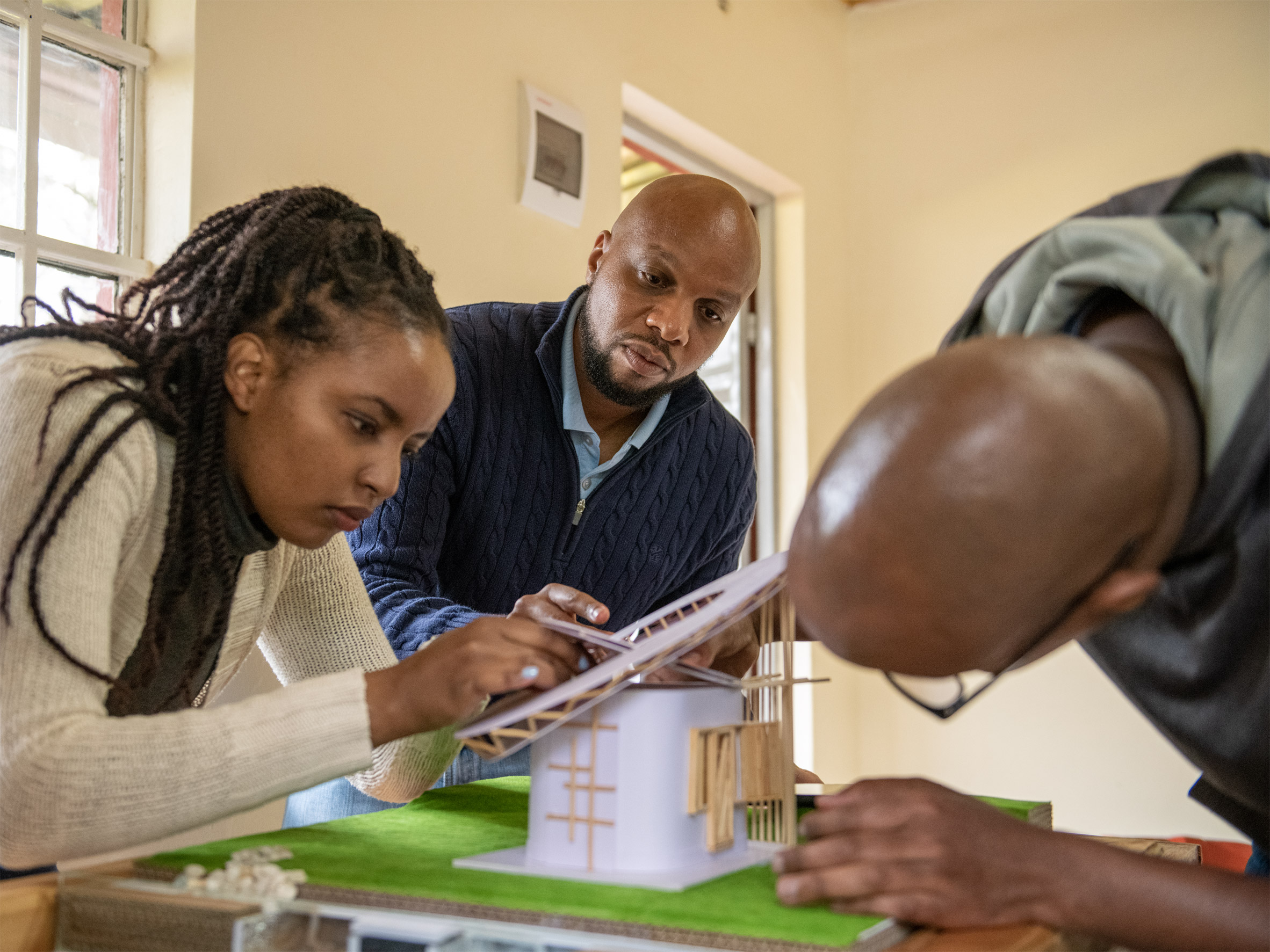

"During the workshops at INTERSECT BY LEXUS - NYC, the mentors helped us think about how to break down our problem and provide a prototype solution, all while building design and leadership principles throughout the process," said BellTower's John Kamau.
"Our Lexus Design Award experience has taught us invaluable lifelong lessons. All our future designs will be aligned with the key principles as part of the Lexus family."
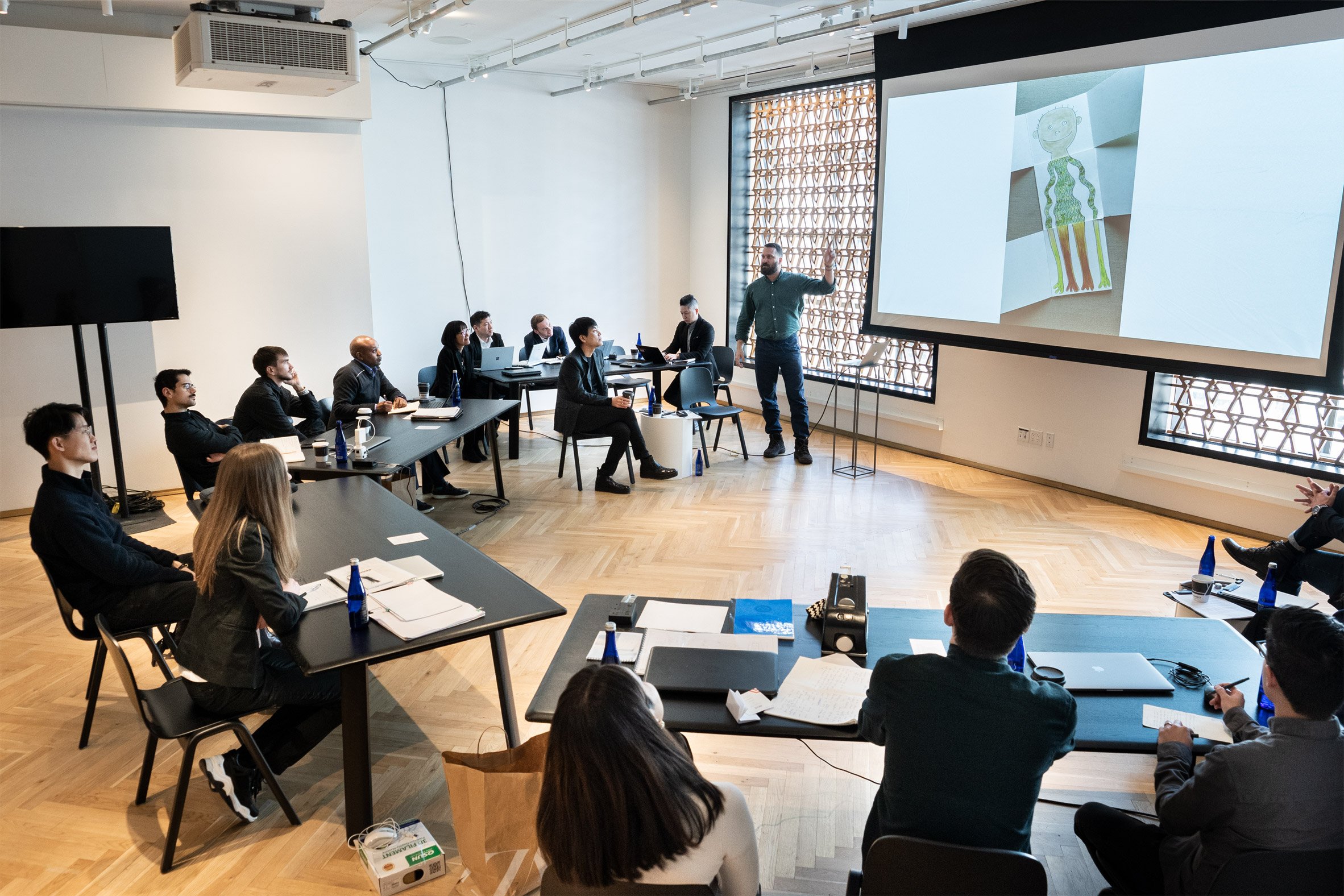

For mentor and New York designer Doucet, the decision to award BellTower the 2020 prize was no surprise.
He said that it was "telling that the winner the judges chose had the largest transformation in terms of clarifying and solidifying their idea throughout the course of the mentorship program."
"The Open Source team took to heart the comments, questions and concerns of the group of mentors and reacted decisively in turn. The judges, of course, were unaware of this but the result was reflected in the final proposal," he concluded.

Find out more about the Lexus Design Award on the company's website. The Lexus Design Award 2021 is now open for entries until October 11.
The post African design studio BellTower wins Lexus Design Award 2020 appeared first on Dezeen.
from Dezeen https://ift.tt/2EXhfAa